
This article is written for the benefit of Resident Taxpayers of Singapore.
If you are a non-resident taxpayer of Singapore (eg. Taylor Swift), click here.
It’s the time of the year again, the income tax season!
If you are once again troubled by the process of filing for your personal income tax, fret not because this article will serve as your 101 guide of how much tax you will have to pay and what reliefs you might qualify for.
For new entrants to the workforce, the Year of Assessment 2024 (YA 2024), refers to income earned from the previous calendar year 1 Jan to 31 Dec 2023.
The filing deadline for YA 2024 are as follows:
- 15 April 2024 for paper filing
- 18 April 2024 for e-filing
So how much Income Tax will you have to pay?
This is dependent on these 2 factors:
- Whether you are classified as a tax resident or non-resident
- How much you earn in Singapore
Let us look at the criteria to being a tax resident.
Tax Resident:
Income Tax rates depend on an individual’s tax residency status.
You will be treated as a tax resident for a particular Year of Assessment if you are:
#1: A Singapore Citizen or Singapore Permanent Resident who resides in Singapore except for temporary absences;
#2: A foreigner who has stayed/ worked in Singapore:
- For at least 183 days in the previous calendar year; or
- Continuously for 3 consecutive years, even if the period of stay in Singapore may be less than 183 days in the first year and/ or third year;
#3: A foreigner who has worked in Singapore for a continuous period straddling 2 calendar years and the total period of stay is at least 183 days*. This applies to employees who entered Singapore but excludes directors of a company, public entertainers, or professionals.
*including your physical presence immediately before and after your employment
Foreigners who are issued a work pass with a minimum validity of 1 year will also be considered as tax residents.
If you do not meet the conditions stated above, you will be treated as a non-resident of Singapore for tax purposes.
(Source: IRAS – Basics Of Individual Income Tax)
Tax Rates:
Let us now dive into tax filing for a resident taxpayer.
Singapore adopts a progressive tax system for their resident taxpayers. This means that the tax rates increase as the income levels rise. As shown in the image below, the higher your chargeable income, the higher your gross tax payable.

Source: IRAS Income Tax Calculator
Determining your Chargeable Income:
To determine your chargeable income, we need to first define what is considered as “Income“.
“Income” refers to:
- Employment Income
- Trade income for the accounting year (for self-employed activities); and/ or
- Other income such as rental income
Next, we will consider the available tax deductions and reliefs. Singapore offers various tax deductions and reliefs for their tax residents to help reduce their tax burden.
Tax deductions refer to any allowable expenses or approved donations you made during the year of assessment.
An individual’s allowable expense is defined according to the individual’s employment type.
Allowable Employment Expenses (Employed):
- Incurred while carrying our your official duties;
- Not reimbursed by your employer; and
- Not capital or private in nature
Source: IRAS – Employment Expenses
Allowable Business Expenses (Self-Employed):
- Expenses must be incurred. An expense is “incurred” when the legal liability to pay has arisen, regardless of the date of actual payment of the money;
- Expenses must be related to your business. You must be able to show why you need to incur the expenditure to earn the income;
- Expenses that are personal and private in nature are not allowable as they do not relate to your business;
- Expenses that are capital in nature (e.g. purchase of fixed assets such as plant and machinery) are not allowable business expenses. However, depreciation of fixed assets may be claimed as capital allowances
- Expenses should be supported by proper and complete source documents that should be kept for at least 5 years to substantiate your claims
Approved Donations:
Donations to Community Chest, CDAC, MUIS, SINDA, or any approved Institution of a Public Character (IPC) will qualify you for tax deductions.
Note that only donations to a charity which is an approved IPC in Singapore for causes that benefit the local community will be recognised.
Remember to provide your particulars (NRIC/FIN) to the IPC so that your eligible donation is transmitted to IRAS for auto-inclusion in your tax returns.
Tax Reliefs:
The available tax reliefs for resident taxpayers are as follows. We have grouped them into 3 broad categories.
These tax reliefs may be eligible to you if you are employed:
- Earned Income Relief
- CPF Relief for Employees
- CPF Relief for Self-Employed
These tax reliefs may eligible to you if you have a dependent at home:
- Spouse Relief/ Handicapped Spouse Relief
- Foreign Domestic Worker Levy Relief
- Parent Relief/ Handicapped Parent Relief
- Grandparent Caregiver Relief
- Qualifying Child Relief (QCR)/ Handicapped Child Relief (HCR)
- Working Mother’s Child Relief (WMCR)
- Handicapped Brother/ Sister Relief
These tax reliefs are eligible for the individual taxpayer:
- Life Insurance Relief
- Course Fees Relief
- SRS Contributions and Tax Relief
- CPF Cash Top-up Relief
- Compulsory and Voluntary Medisave Contributions
- NSman Relief (Self, Wife and Parent)
Visit the IRAS – Tax Reliefs Rebates and Deductions for a complete explanation of the individual reliefs and their specific requirements.

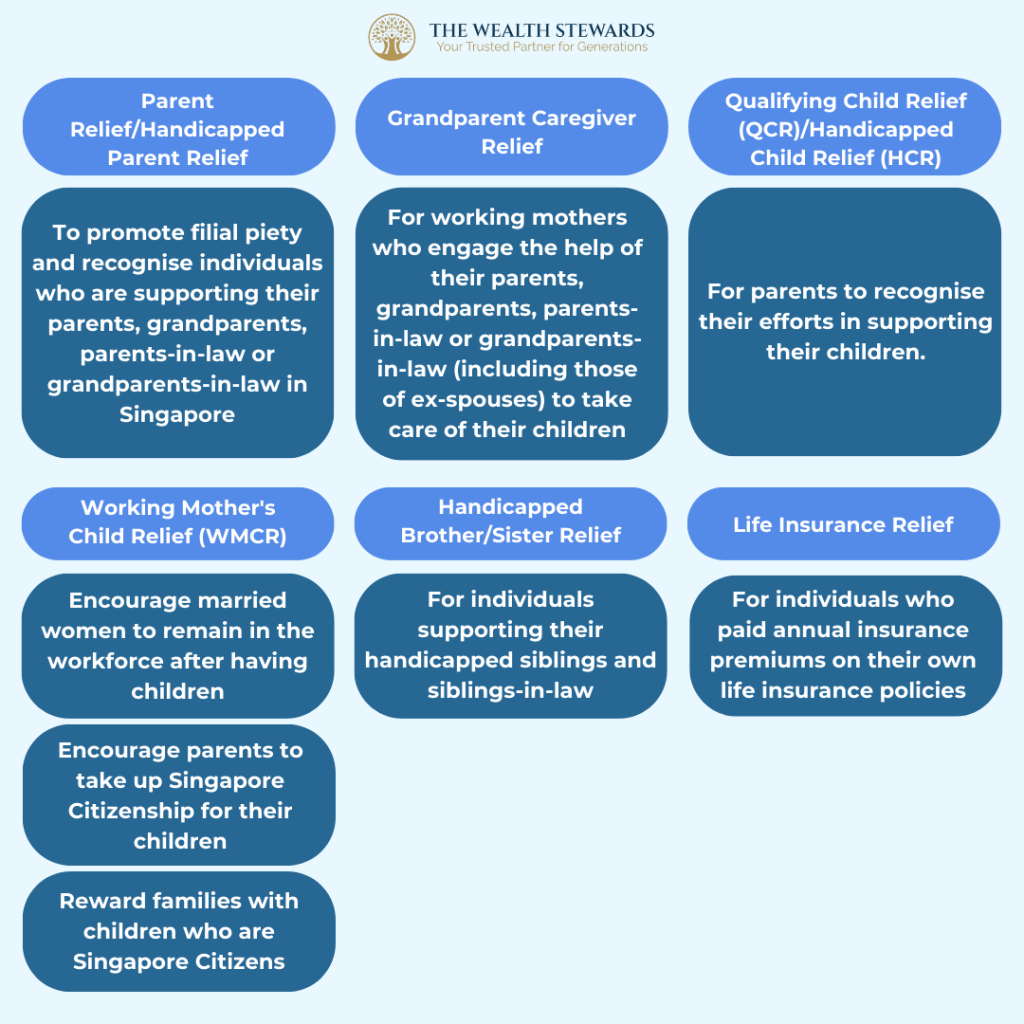
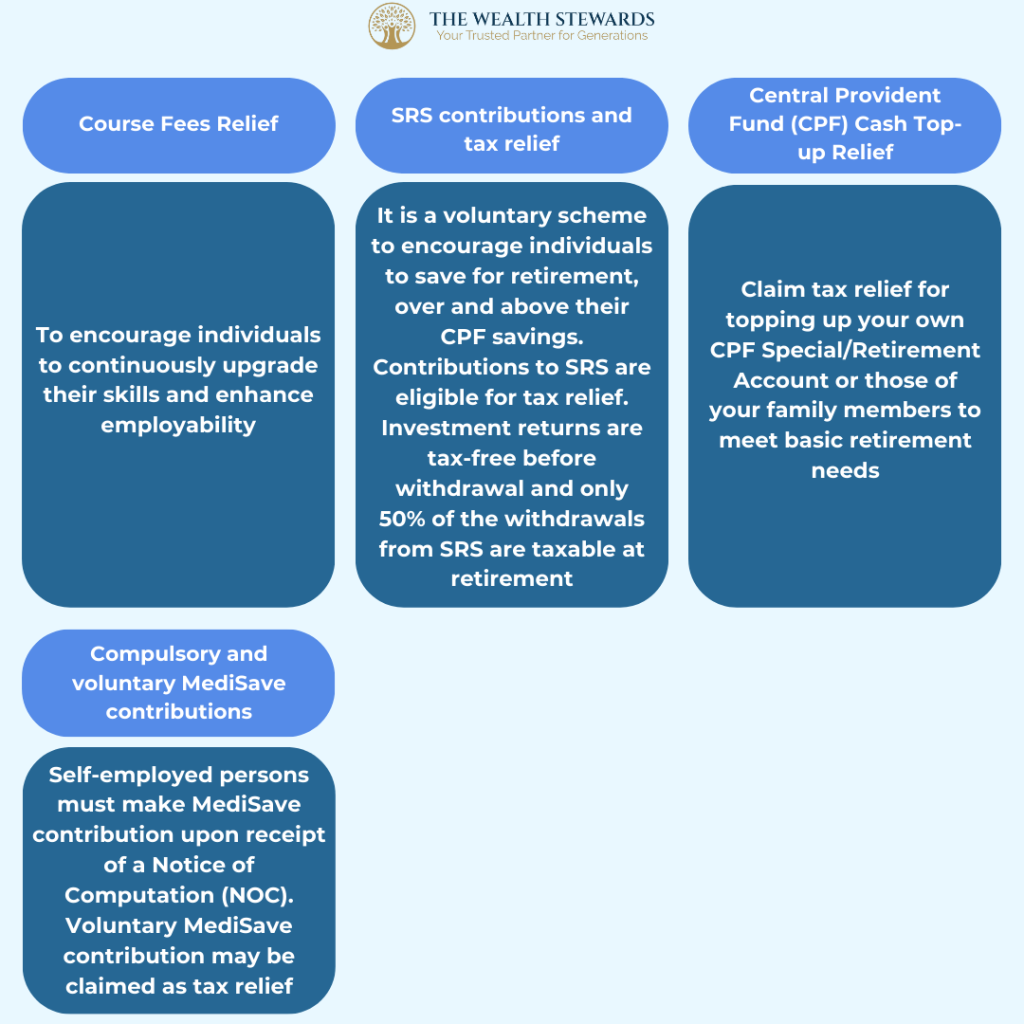
Source: IRAS – Tax Reliefs
From time to time, the Singapore Government may introduce personal income tax rebates to provide relief to taxpayers. These tax rebates are usually announced during the annual Budget speech and can vary in amount and eligibility criteria.
Note:
- Only tax residents (including non-Singaporean Citizens who are in Singapore for more than 183 days in a year) can claim for tax relief. Check if you meet the qualifying conditions using the Relief Checker.
- The total amount of Personal Income Tax Relief cannot exceed the relief cap of SGD $80,000.
Filing your Personal Income Tax:
For the AY 2024, you will fall under 3 categories. Use the image below to find out if you are required to file for your personal income tax.
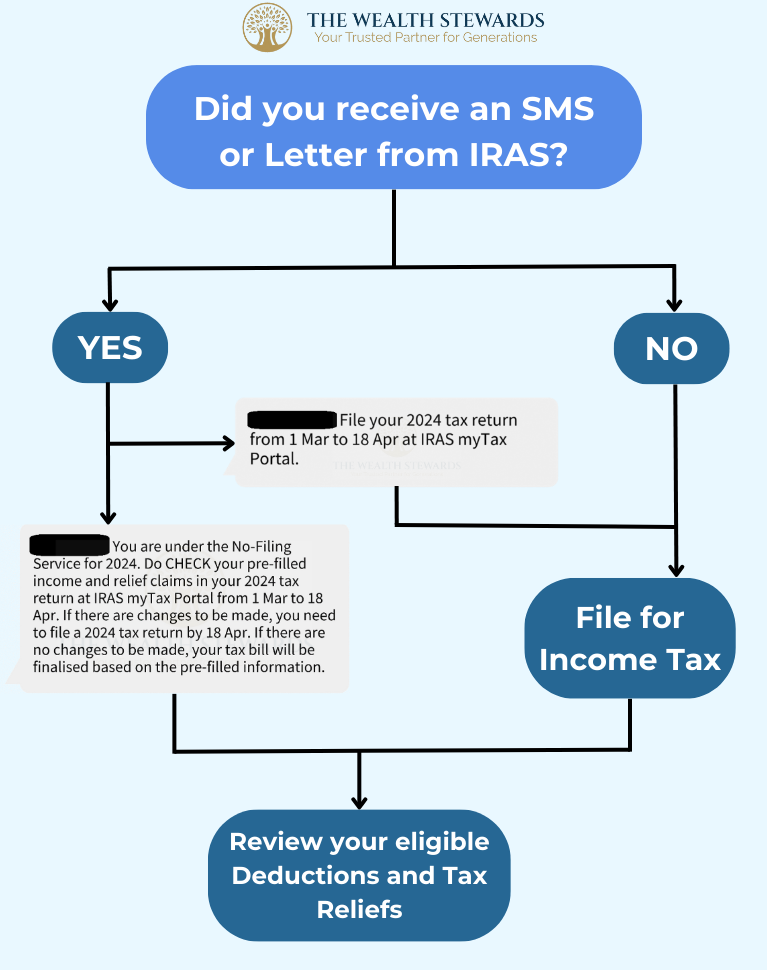
As a rule of thumb, you will have to file for personal income tax if:
- Your annual income (inclusive of rental income) was more than SGD $22,000 in the previous year; OR
- Your annual self-employed income exceeded SGD $6,000 in the previous year
Things to note if you are a Self-Employed Individual:
When it comes to income tax filing, self-employed individuals are handled differently than employees in a company. For example, an employee is not permitted to claim trade losses against trade income; however, a self-employed individual may.
Self-employed individuals should also file their taxes under “Trade, Business, Profession or Vocation” instead of “Individual Income Tax”.
The table below shows the difference between an employee and a self-employed individual.

Self-employed individuals can opt for pre-filing of their income as well. While this might be a tedious task, this one-off hassle will positively benefit your future income tax filing experience. Click here to find out more on how to pre-file your income tax: IRAS – Pre-Filling Of Income For Self-Employed Persons.
Still confused about filing your income tax?
The IRAS website consists of a few neat tools accessible for the public use to better the tax filing experience.
#1 Filing Checker
To check if you require to file for income tax, you can head here: IRAS – Filing Checker
This allows you to check if you are required to file your income tax for the Year of Assessment 2024 (income earned n 2023), based on information provided by you.
Alternatively, you may login to myTax Portal using your Singpass to view if a tax return has been issued to you.
#2 Tax Calculator
Another useful tool that is accessible on the IRAS website is the Tax Calculator.
This excel sheet will you determine your “Chargeable Income” and “Net Tax Payable”.
To access the calculator, click on the link here and choose the relevant Year of Assessment (YA):
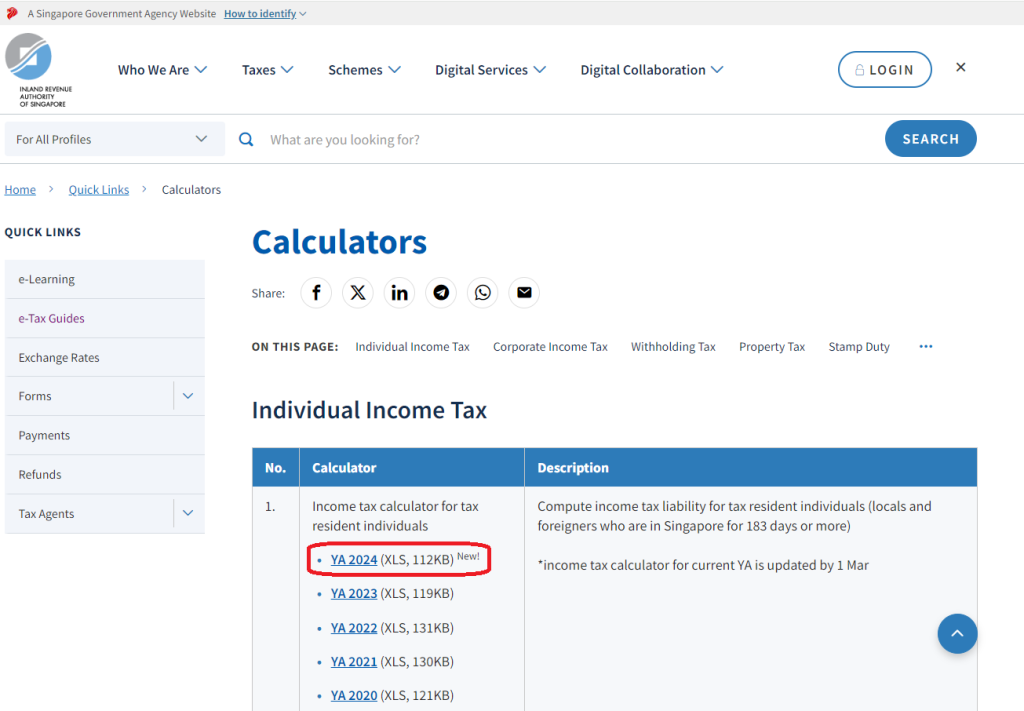
Source: IRAS – Tax Calculator
The image below shows how the calculator looks like:

Source: IRAS – Tax Calculator
Hovering your cursor over the individual personal relief “entry box” will also show the explanation of the relief and the requirements to qualify for the relief.
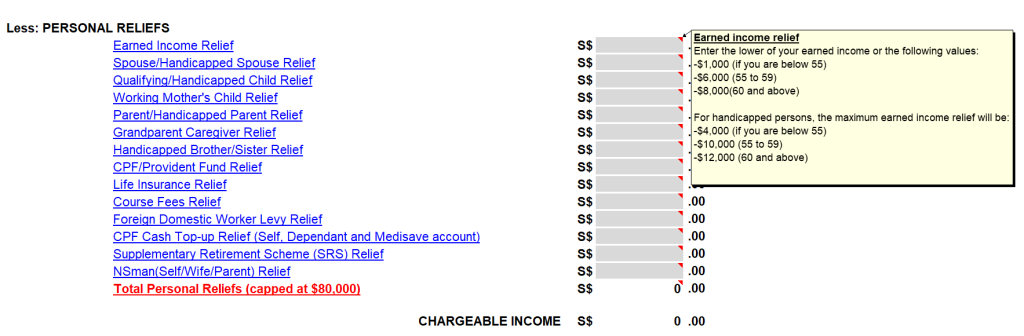
Source: IRAS – Tax Calculator
#3 IRAS Live Chat
Lastly, the IRAS website has a live chat function for users to pose questions and get an immediate response.
This feature is recommended for individuals who are in unique positions and would require an IRAS Tax Officer’s assistance.
Click here to visit the IRAS contact page and follow the images below to assess the live chat function.
Source: IRAS – Contact Us
Scroll down the website page until you find this button. Click on it.
Source: IRAS – Contact Us
Select the relevant department that you require assistance from.
Source: IRAS – Contact Us
Type down your question and click “start chat” to start chatting. An IRAS Tax Officer will review your question and respond to your immediately.
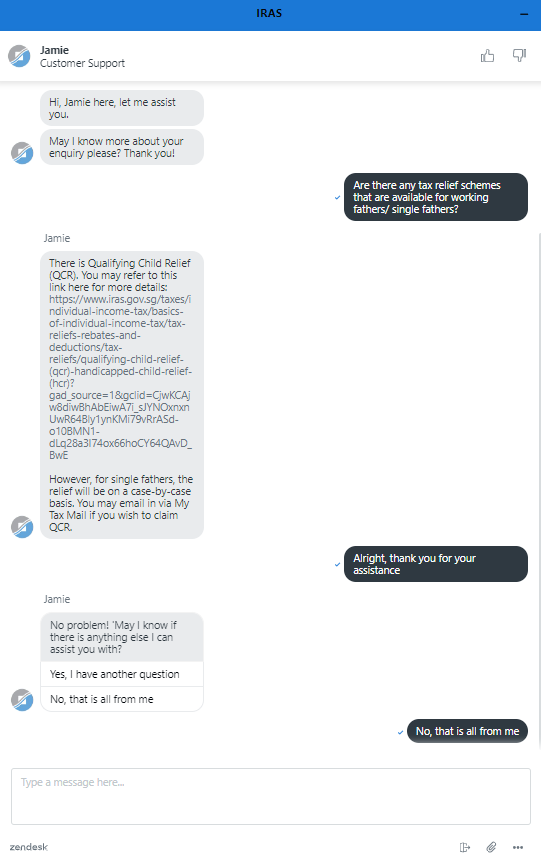
Source: IRAS – Contact Us
The above image is an example of the IRAS live chat function
These tools are free and available for everyone to utilise. Use these tools to your advantage and ease your tax filing experience!
Ending Note: Tax Avoidance and Evasion
Singapore has strict laws against tax evasion and avoidance.
Tax evasion which is the deliberate evasion of tax obligations through illegal means is a criminal offence.
Tax avoidance which is the exploitation of legal loopholes to minimise tax liabilities is closely monitored by IRAS. measures are taken place to prevent abusive tax planning schemes.
With the filing deadline for YA 2024 fast approaching, the team at TWSG wishes you a smooth-sailing tax filing experience and do remember to file your taxes on time or apply for the necessary time extension to avoid the unnecessary payment of fines!
Disclaimer:
Members of TWSG are not professional tax advisors. If you require specific guidance for your unique tax processing, please approach your TWSG Wealth Manager to refer you to a qualified accountant or tax professional.
If you enjoyed this article, TWSG will be holding our quarterly seminar on the evening of 18 April 2024 to share about 2024 market updates as well as how to build your passive income.

Authors:
Shawn Ong

Aaron Ang

Edited by:
Yee Shen Hao

![]()





